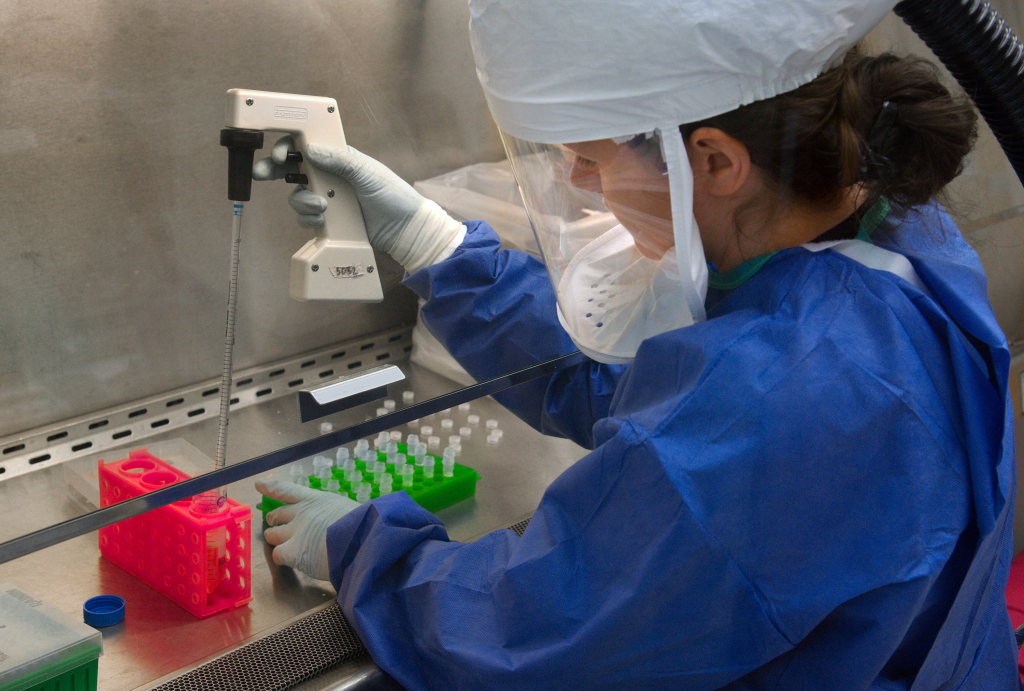
Radiotherapy is one of the most common therapeutic methods employed for human cancer treatment. This method uses ionizing radiation, which mainly acts indirectly via the radiolysis products of water damaging cellular DNA. Commonly used radiotherapy causes many side effects. Two classes of radiosensitizing agents are distinguished: hypoxic cell sensitizers, which rely on hypoxia occurring only in cancer cells, and pyrimidine analogues that could be incorporated into DNA due to their structural similarity to native nucleosides.
The method allowing to increase
the effectiveness of radiotherapy is the use of the respective derivatives of nucleic bases radiosensitizers, operating in a low oxygen environment, that are incorporated into cellular DNA during its biosynthesis.